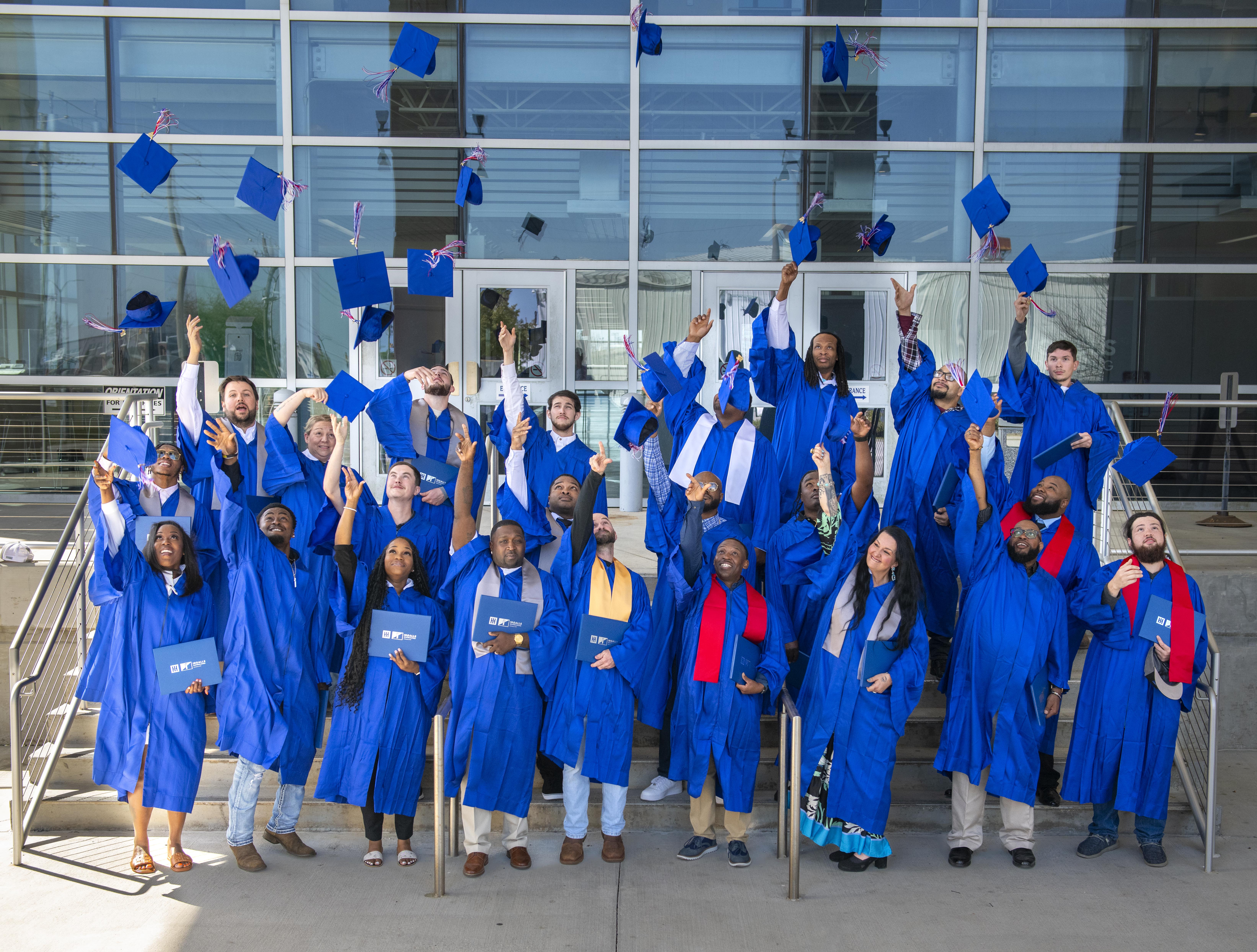
Since 1952, the Apprentice School has produced more than 4,000 graduates in support of Ingalls’ operational needs. The program involves comprehensive three- to four-year curriculum for students interested in shipbuilding careers. Our graduates have held many types of positions from pipe welders to senior executives. Our faculty and staff deliver instructions for our programs and course offerings that enable apprentices to gain not only the skills, knowledge and pride of workmanship, but also the educational foundation and personal qualities needed to fully meet the challenges of a shipbuilding career.

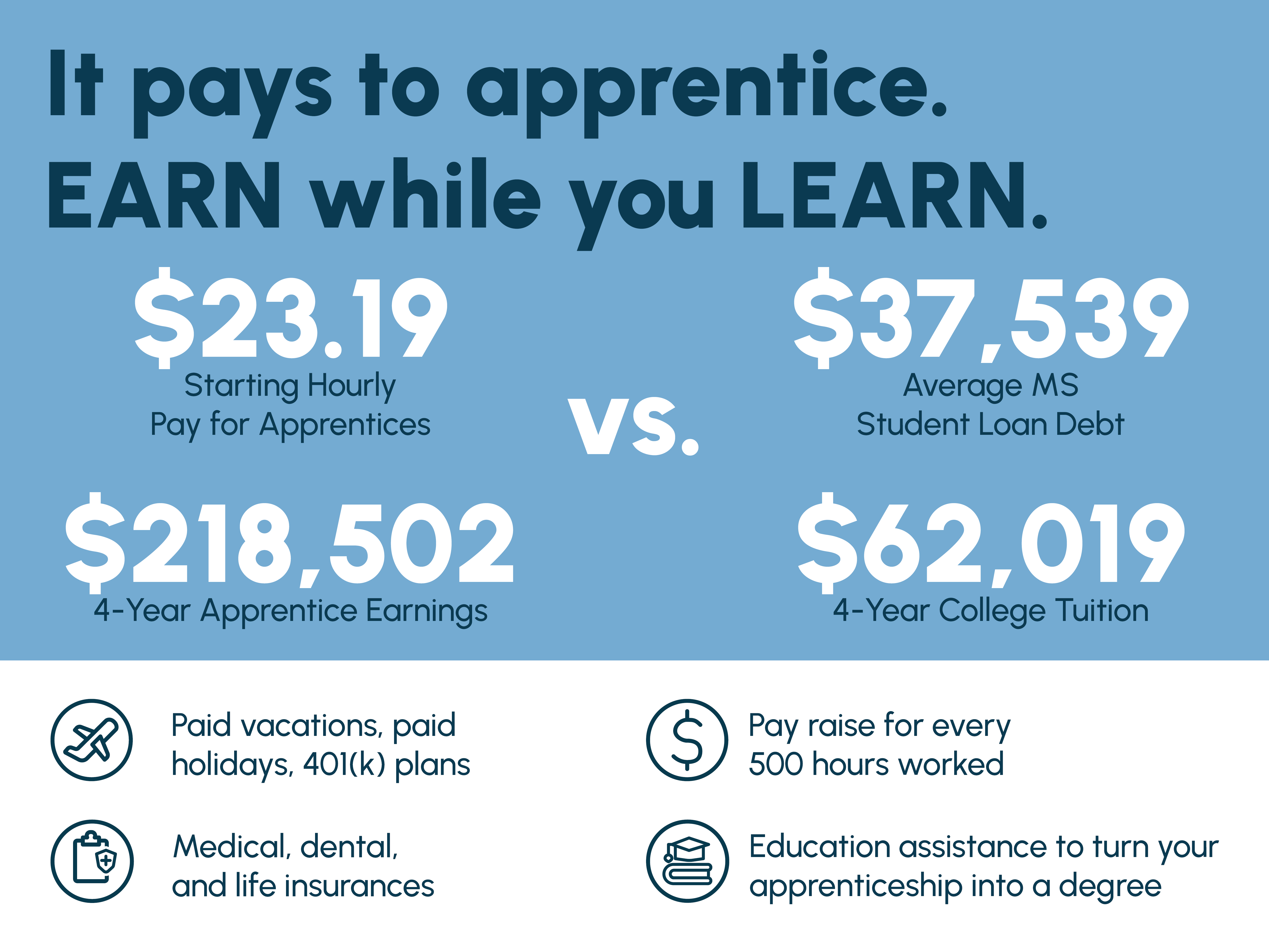
Advancement in the apprenticeship wage schedule is based on the length of participation in the program. All overtime hours go towards the apprentice’s hours worked. Apprentices attend class 1 day per week for 4.5 hours.



| Semester: 1 |
| Course: Technical Math |
| Hours: 72 |
| Covers major aspects of practical math including basic arithmetic, trigonometry, and geometry. |
| Semester: 2 |
| Course: Introduction to Shipbuilding and Blueprints |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course provides instruction in basic shipbuilding, blueprint reading and the process of ship design and planning. |
| Semester: 3 |
| Course: Blueprint Reading for Shipfitters |
| Hours: 40 |
| This course is designed to introduce the apprentice to blueprint reading techniques and principles. This course covers in detail all the major areas of blueprint reading required by the specified craft. |
| Semester: 4 |
| Course: Fundamentals of Drafting |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to introduce the apprentice to graphic language from the basics of free-hand sketches to multi-view and working drawings using the most common tools of the drafting trade. |
| Semester: 5 |
| Course: Naval Architecture and Ship Structure |
| Hours: 72 |
| Principles of ship construction and terminology. |
| Semester: 6 |
| Course: Marine System Integration |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to provide the basic information that an apprentice must understand on how major marine systems operate and function along with the shipboard equipment. |
| Semester: 7 |
| Course: Journeyman Essentials for Shipfitters |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to introduce various cutting and burning processes, plasma arc cutting, advanced structural print reading, fitting, reference control lines and basic level surveying. The apprentice will be able to successfully and safely demonstrate proper Ingalls Shipbuilding practices and procedures to NAVAL requirements. |
| Semester: 1 |
| Course: Technical Math |
| Hours: 72 |
| Covers major aspects of practical math including basic arithmetic, trigonometry, and geometry. |
| Semester: 2 |
| Course: Introduction to Shipbuilding and Blueprints |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course provides instruction in basic shipbuilding, blueprint reading and the process of ship design and planning. |
| Semester: 3 |
| Course: Blueprint Reading for Carpenters |
| Hours: 40 |
| This course is a comprehensive guide to interpreting drawings commonly found in the shipbuilding industry. This course covers in detail all the major areas of blueprint reading required by the specified craft. |
| Semester: 4 |
| Course: Carpentry Shop I |
| Hours: 72 |
| Emphasis is placed on carpentry orientation and study of hand tools, materials, ethics and history of the trade and operations. |
| Semester: 5 |
| Course: Carpentry Shop II |
| Hours: 72 |
| Principles of ship construction and terminology. |
| Semester: 6 |
| Course: Naval Architecture and Ship Structure |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to provide the basic information that an apprentice must understand on how major marine systems operate and function along with the shipboard equipment. |
| Semester: 7 |
| Course: Fundamentals of Drafting |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to introduce the apprentice to graphic language from the basics of free-hand sketches to multi-view and working drawings using the most common tools of the drafting trade. |
| Semester: 8 |
| Course: Principles of Management |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to prepare the graduating apprentice to be a leader in the company. The course covers the “day to day” operations of a foremen as well as training scenarios designed to prepare the apprentice for situations he/she will face in a manager’s role. |
| Semester: 9 |
| Course: Production Control and Planning |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course provides managerial information regarding material requirements, capacity planning and control techniques, master production scheduling, and techniques in cost analysis. |
| Semester: 1 |
| Course: DC Circuits |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed for students to know the principles and theories associated with DC circuits. This course includes the study of electrical circuits, laws and formulae, and the use of test equipment to analyze DC circuits. |
| Semester: 2 |
| Course: AC Circuits |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to provide students with the principles and theories associated with AC circuits. This course includes the study of electrical circuits, lays and formulae, and the use of test equipment to analyze AC circuits. |
| Semester: 3 |
| Course: Digital Electronics |
| Hours: 72 |
| A course designed to introduce the student to number systems, logic circuits, counters, registers, memory devices, combination logic circuits, Boolean algebra, and a basic computer system. |
| Semester: 4 |
| Course: Solid State Devices and Circuits |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to introduce the student to active devices, which include PN junction diodes, bipolar transistors, bipolar transistor circuits, and unipolar devices with emphasis on low frequency application and troubleshooting. |
| Semester: 5 |
| Course: Solid State Motor Controls |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course covers the principles and operation of solid state motor control as well as the design, installation, and maintenance of different solid state devices for motor control. |
| Semester: 6 |
| Course: Programmable Logic Controllers |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course covers use of programmable logic controllers (PLCs) in modern industrial settings as well as the operating principles of PLCs and practice in the programming, installation, and maintenance of PLCs. |
| Semester: 7 |
| Course: Electronic Communications |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to provide the student with concepts and skills related to analog and digital communications. |
| Semester: 8 |
| Course: Fiber Optics with Marine Capstone |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course will serve as a capstone to the formal electrical apprenticeship educational experience. Students will review subject matter from all previous coursework and OJT experiences. The course will provide for an extensive demonstration of competencies learned throughout this period of time in the apprenticeship encompassing both training and education. |
| Semester: 1 |
| Course: Technical Math |
| Hours: 72 |
| Covers major aspects of practical math including basic arithmetic, trigonometry, and geometry. |
| Semester: 2 |
| Course: Introduction to Shipbuilding and Blueprints |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course provides instruction in basic shipbuilding, blueprint reading and the process of ship design and planning. |
| Semester: 3 |
| Course: Blueprint Reading for Machinists |
| Hours: 40 |
| This course is designed to introduce the apprentice to blueprint reading techniques and principles. This course covers in detail all the major areas of blueprint reading required by the specified craft. |
| Semester: 4 |
| Course: Precision Layout |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to provide the basic information that an apprentice must acquire in order to use precision tools such as micrometers in today’s machinist trade. |
| Semester: 5 |
| Course: Power Machinery |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to provide the basic information that an apprentice must acquire in order to use the standard hand and machine tools found in today’s machinist trade. |
| Semester: 6 |
| Course: Mechanical Maintenance |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course provides instruction of the basic principles of mechanical systems. |
| Semester: 7 |
| Course: Fundamentals of Drafting |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to introduce the apprentice to graphic language from the basics of free-hand sketches to multi-view and working drawings using the most common tools of the drafting trade. |
| Semester: 8 |
| Course: Marine System Integration |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to provide the basic information that an apprentice must understand on how major marine systems operate and function along with the shipboard equipment. |
| Semester: 9 |
| Course: Naval Architecture and Ship Structure |
| Hours: 72 |
| Principles of ship construction and terminology. |
| Semester: 1 |
| Course: Technical Math |
| Hours: 72 |
| Covers major aspects of practical math including basic arithmetic, trigonometry, and geometry. |
| Semester: 2 |
| Course: Introduction to Shipbuilding and Blueprints |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course provides instruction in basic shipbuilding, blueprint reading and the process of ship design and planning. |
| Semester: 3 |
| Course: Blueprint Reading for Pipe Insulator |
| Hours: 40 |
| This course is designed to introduce the apprentice to blueprint reading techniques and principles. This course covers in detail all the major areas of blueprint reading required by the specified craft. |
| Semester: 4 |
| Course: Metal Lagging |
| Hours: 36 |
| This course is designed to instruct the apprentice on how to layout sheet metal for the lagging process on insulated piping or ducting systems. |
| Semester: 5 |
| Course: Safety, Health & Environment |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to provide knowledge and skills to reinforce attitudes and behaviors required for safe and environmentally sound work habits. |
| Semester: 6 |
| Course: Naval Architecture and Ship Structure |
| Hours: 72 |
| Principles of ship construction and terminology. |
| Semester: 7 |
| Course: Fundamentals of Drafting |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to introduce the apprentice to graphic language from the basics of free-hand sketches to multi-view and working drawings using the most common tools of the drafting trade. |
| Semester: 8 |
| Course: Project Management |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to provide the apprentice with the foundation skills needed to understand roles and responsibilities of construction, supervision and managing projects. |
| Semester: 1 |
| Course: Technical Math |
| Hours: 72 |
| Covers major aspects of practical math including basic arithmetic, trigonometry, and geometry. |
| Semester: 2 |
| Course: Introduction to Shipbuilding and Blueprints |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to introduce the apprentice to blueprint reading techniques and principles. This course covers in detail all the major areas of the design of the ships structure. This course also covers the basic blueprint reading required by the craft.nstruction in basic shipbuilding, blueprint reading and the process of ship design and planning. |
| Semester: 3 |
| Course: Blueprint Reading for Joiners |
| Hours: 40 |
| This course is designed to introduce the apprentice to blueprint reading techniques and principles. This course covers in detail all the major areas of blueprint reading required by the specified craft. |
| Semester: 4 |
| Course: Metal Lagging |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to introduce the apprentice on how to use hand and shop machine tools safely. Also teaching the apprentice how to layout basic design within the sheetmetal craft using blue print, written instruction, or verbal instruction. |
| Semester: 5 |
| Course: Layout II |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to extend the apprentices education on layout, enabling the apprentice to be challenged with more complex blue prints, verbal instruction, written instruction to be able to designs with sheetmetal. |
| Semester: 6 |
| Course: Fundamentals of Drafting |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to introduce the apprentice to graphic language from the basics of free-hand sketches to multi-view and working drawings using the most common tools of the drafting trade. |
| Semester: 7 |
| Course: Naval Architecture and Ship Structure |
| Hours: 72 |
| Principles of ship construction and terminology. |
| Semester: 8 |
| Course: Principles of Management |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to prepare the graduating apprentice to be a leader in the company. The course covers the “day to day” operations of a foremen as well as training scenarios designed to prepare the apprentice for situations he/she will face in a manager’s role. |
| Semester: 9 |
| Course: Production Planning and Control |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course provides managerial information regarding material requirements, capacity planning and control techniques, master production scheduling, and techniques in cost analysis. |
| Semester: 1 |
| Course: Technical Math |
| Hours: 72 |
| Covers major aspects of practical math including basic arithmetic, trigonometry, and geometry. |
| Semester: 2 |
| Course: Introduction to Shipbuilding and Blueprints |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course provides instruction in basic shipbuilding, blueprint reading and the process of ship design and planning. |
| Semester: 3 |
| Course: Blueprint Reading for Machinists |
| Hours: 40 |
| This course is designed to introduce the apprentice to blueprint reading techniques and principles. This course covers in detail all the major areas of blueprint reading required by the specified craft. |
| Semester: 4 |
| Course: Precision Layout |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to provide the basic information that an apprentice must acquire in order to use precision tools such as micrometers in today’s machinist trade. |
| Semester: 5 |
| Course: Power Machinery |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to provide the basic information that an apprentice must acquire in order to use the standard hand and machine tools found in today’s machinist trade. |
| Semester: 6 |
| Course: Mechanical Maintenance |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to provide the basic information that an apprentice must acquire in order to repair shipboard equipment in today’s machinist trade. |
| Semester: 7 |
| Course: Fundamentals of Drafting |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to introduce the apprentice to graphic language from the basics of free-hand sketches to multi-view and working drawings using the most common tools of the drafting trade. |
| Semester: 8 |
| Course: Marine System Integration |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to provide the basic information that an apprentice must understand on how major marine systems operate and function along with the shipboard equipment. |
| Semester: 9 |
| Course: Naval Architecture and Ship Structure |
| Hours: 72 |
| Principles of ship construction and terminology. |
| Semester: 1 |
| Course: Surface Preparation |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to introduce the apprentice to abrasive blasting techniques, machine cleaning and other means of surface preparation as well as the pretreatment of the different types of surfaces used marine applications. Upon completion of this course the apprentice will receive their SSPC-QP1 certification card. |
| Semester: 2 |
| Course: Spray Painting |
| Hours: 72 |
| An introduction of the use of coating systems for the protection of steel surfaces, describes powder coating, materials, application methods, substrates and curing techniques. |
| Semester: 3 |
| Course: Environmental Health and Safety |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to provide the apprentice with the basic information needed to understand safety problems within the painting trade. The apprentice will also gain a better understanding of environmental issues and how they are responsible for safety and reducing environmental issues. |
| Semester: 4 |
| Course: Inspection Fundamentals |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to instruct the apprentices on proper job inspection techniques. The apprentices will also be taught what constitutes as marine coating quality defects and how to recognize defects. Apprentice will be instructed on proper procedures when using test equipment and instruments needed to verify compliance with inspection standards. |
| Semester: 5 |
| Course: Naval Architecture and Ship Structure |
| Hours: 72 |
| Principles of ship construction and terminology. |
| Semester: 6 |
| Course: Principles of Management |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to prepare the graduating apprentice to be a leader in the company. The course covers the “day to day” operations of a foremen as well as training scenarios designed to prepare the apprentice for situations he/she will face in a manager’s role. |
| Semester: 1 |
| Course: Welding Theory and Techniques |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to give the apprentice the basic knowledge of the shielded Metal Arc (SMAW), Gas Tungsten Arc (GTAQ) and Gas Metal Arc (GMAQ) welding processes. |
| Semester: 2 |
| Course: Naval Architecture and Ship Structure |
| Hours: 72 |
| Principles of ship construction and terminology. |
| Semester: 3 |
| Course: Pipe Welding Shop |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to teach the apprentice the safe and proper techniques for: Burning, Plasma Arc Cutting, Carbon Arc Gouging and Mirror Welding. |
| Semester: 4 |
| Course: Marine System Integration |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to give the Apprentice the basic knowledge of the welding procedures used at Ingalls Shipbuilding. |
| Semester: 5 |
| Course: Introduction to Shipbuilding and Blueprints |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course provides instruction in basic shipbuilding, blueprint reading and the process of ship design and planning. |
| Semester: 6 |
| Course: Blueprint Reading for Pipe |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to introduce the apprentice to blueprint reading techniques and principles. This course covers in detail all the major areas of blueprint reading required by the specified craft. |
| Semester: 7 |
| Course: Principles of Management |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to prepare the graduating apprentice to be a leader in the company. The course covers the “day to day” operations of a foremen as well as training scenarios designed to prepare the apprentice for situations he/she will face in a manager’s role. |
| Semester: 1 |
| Course: Technical Math |
| Hours: 72 |
| Covers major aspects of practical math including basic arithmetic, trigonometry, and geometry. |
| Semester: 2 |
| Course: Naval Architecture and Ship Structure |
| Hours: 72 |
| Principles of ship construction and terminology. |
| Semester: 3 |
| Course: Introduction to Shipbuilding and Blueprints |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course provides instruction in basic shipbuilding, blueprint reading and the process of ship design and planning. |
| Semester: 4 |
| Course: Blueprint Reading for Pipe |
| Hours: 40 |
| This course is designed to introduce the apprentice to blueprint reading techniques and principles. This course covers in detail all the major areas of blueprint reading required by the specified craft. |
| Semester: 5 |
| Course: Marine Pipefitting |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to teach the Marine Pipefitter the basic fundamentals of the pipe trade. Subjects will include pipe tools and their uses, pipe and pipe material, valves, and pipe fabrication techniques. |
| Semester: 6 |
| Course: Fundamentals of Drafting |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to introduce the apprentice to graphic language from the basics of free-hand sketches to multi-view and working drawings using the most common tools of the drafting trade. |
| Semester: 7 |
| Course: Marine System Integration |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to teach the basics of the steam power plan, major piping systems, gas turbine plant, nuclear power plant and the central operations system. |
| Semester: 8 |
| Course: Production Planning and Control |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course provides managerial information regarding material requirements, capacity planning and control techniques, master production scheduling, and techniques in cost analysis. |
| Semester: 9 |
| Course: Principles of Management |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to prepare the graduating apprentice to be a leader in the company. The course covers the “day to day” operations of a foremen as well as training scenarios designed to prepare the apprentice for situations he/she will face in a manager’s role. |
| Semester: 1 |
| Course: Technical Math |
| Hours: 72 |
| Covers major aspects of practical math including basic arithmetic, trigonometry, and geometry. |
| Semester: 2 |
| Course: Introduction to Shipbuilding and Blueprints |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course provides instruction in basic shipbuilding, blueprint reading and the process of ship design and planning. |
| Semester: 3 |
| Course: Naval Architecture and Ship Structure |
| Hours: 72 |
| Principles of ship construction and terminology. |
| Semester: 4 |
| Course: Marine System Integration |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to teach the basics of the steam power plan, major piping systems, gas turbine plant, nuclear power plant and the central operations system. |
| Semester: 5 |
| Course: Production Planning and Control |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course provides managerial information regarding material requirements, capacity planning and control techniques, master production scheduling, and techniques in cost analysis. |
| Semester: 6 |
| Course: Principles of Management |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to prepare the graduating apprentice to be a leader in the company. The course covers the “day to day” operations of a foremen as well as training scenarios designed to prepare the apprentice for situations he/she will face in a manager’s role. |
| Semester: 7 |
| Course: Trade Specific Certification |
| Hours: 72 |
| TBD |
| Semester: 8 |
| Course: Quality Training & Certification |
| Hours: 72 |
| TBD |
| Semester: 1 |
| Course: Technical Math |
| Hours: 72 |
| Covers major aspects of practical math including basic arithmetic, trigonometry, and geometry. |
| Semester: 2 |
| Course: Introduction to Shipbuilding and Blueprints |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course provides instruction in basic shipbuilding, blueprint reading and the process of ship design and planning. |
| Semester: 3 |
| Course: Rigger Shop 1 |
| Hours: 72 |
| Emphasis is placed on carpentry orientation and study of hand tools, materials, ethics and history of the trade and operations. |
| Semester: 4 |
| Course: Rigger Shop 2 |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to make the Carpenter apprentice well-rounded with studies in interior finish, cabinet making, and blueprint reading and estimating. |
| Semester: 5 |
| Course: Naval Architecture and Ship Structure |
| Hours: 72 |
| Principles of ship construction and terminology. |
| Semester: 6 |
| Course: Fundamentals of Drafting |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to introduce the apprentice to graphic language from the basics of free-hand sketches to multi-view and working drawings using the most common tools of the drafting trade. |
| Semester: 7 |
| Course: Principles of Management |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to prepare the graduating apprentice to be a leader in the company. The course covers the “day to day” operations of a foremen as well as training scenarios designed to prepare the apprentice for situations he/she will face in a manager’s role. |
| Semester: 8 |
| Course: Production Planning and Control |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course provides managerial information regarding material requirements, capacity planning and control techniques, master production scheduling, and techniques in cost analysis. |
| Semester: 1 |
| Course: Technical Math |
| Hours: 72 |
| Covers major aspects of practical math including basic arithmetic, trigonometry, and geometry. |
| Semester: 2 |
| Course: Introduction to Shipbuilding and Blueprints |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course provides instruction in basic shipbuilding, blueprint reading and the process of ship design and planning. |
| Semester: 3 |
| Course: Blueprint Reading for SM |
| Hours: 40 |
| This course is designed to introduce the apprentice to blueprint reading techniques and principles. This course covers in detail all the major areas of blueprint reading required by the specified craft. |
| Semester: 4 |
| Course: Naval Architecture and Ship Structure |
| Hours: 72 |
| Principles of ship construction and terminology. |
| Semester: 5 |
| Course: Fundamentals of Drafting |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to introduce the apprentice to graphic language from the basics of free-hand sketches to multi-view and working drawings using the most common tools of the drafting trade. |
| Semester: 6 |
| Course: Layout I |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to instruct the apprentices on safety in relation to hand tools and shop machines. The apprentice will also study basic trade theory in hand processing, machine process and basic layout. |
| Semester: 7 |
| Course: Layout II |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to cover basic principles of parallel and radial line development as related to intermediate Sheetmetal layout work. The apprentice will have to demonstrate layout skill of basic components within the Sheetmetal craft and the Sheetmetal shop. |
| Semester: 8 |
| Course: Layout III |
| Hours: 72 |
| This is an advance Sheetmetal layout course that is designed to cover triangulation method, approaches and solutions to special problems. |
| Semester: 9 |
| Course: Principles of Management |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to provide the apprentice with the foundation skills needed to understand roles and responsibilities of construction, supervision and managing projects. |
| Semester: 1 |
| Course: Introduction to Shipbuilding and Blueprints |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course provides instruction in basic shipbuilding, blueprint reading and the process of ship design and planning. |
| Semester: 2 |
| Course: Naval Architecture and Ship Structure |
| Hours: 72 |
| Principles of ship construction and terminology. |
| Semester: 3 |
| Course: Welding Procedures 1 |
| Hours: 36 |
| This course is designed to introduce to welder apprentices the basic machine types and set up with a Focus on the SMAW / TIG welding processes. |
| Semester: 4 |
| Course: Welding Procedures 2 |
| Hours: 36 |
| This course is designed to introduce welder apprentices to advanced welding principles with a focus on the FCAW/GMAW welding processes. |
| Semester: 5 |
| Course: SMAW and FCAW Processes |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to teach a basic knowledge of the accessory equipment used in semi-automatic welding processes. |
| Semester: 6 |
| Course: Journeyman Essentials for Weld |
| Hours: 36 |
| This course will familiarize the Apprentice with information and knowledge about weld cost, definitions and terms, welding joint design, filler metal selection, welding symbols, visual inspections, and weld defects. In addition, this course will provide the student with the understanding of “Work Orders” and “Physical Progression”. |
| Semester: 7 |
| Course: Principles of Management |
| Hours: 72 |
| This course is designed to prepare the graduating apprentice to be a leader in the company. The course covers the “day to day” operations of a foremen as well as training scenarios designed to prepare the apprentice for situations he/she will face in a manager’s role. |
CLICK EACH POSITION FOR INFORMATION
__PRESENT__PRESENT
__PRESENT
__PRESENT
__PRESENT__PRESENT
__PRESENT
__PRESENT
__PRESENT__PRESENT
__PRESENT
__PRESENT
__PRESENT__PRESENT
__PRESENT
__PRESENT
__PRESENT__PRESENT
__PRESENT
__PRESENT
__PRESENT__PRESENT
__PRESENT
__PRESENT
__PRESENT__PRESENT
__PRESENT
__PRESENT
__PRESENT__PRESENT
__PRESENT
__PRESENT
__PRESENT__PRESENT
__PRESENT
__PRESENT
__PRESENT__PRESENT
__PRESENT
__PRESENT
__PRESENT__PRESENT
__PRESENT
__PRESENT
__PRESENT__PRESENT
__PRESENT
__PRESENT
__PRESENT__PRESENT
__PRESENT
__PRESENT
__PRESENT__PRESENT
__PRESENT
__PRESENT
__PRESENT__PRESENT
__PRESENT
__PRESENT
1. Be at least 18 years of age
2. Submit High School Transcript or GED Transcript with test scores
3. State issued Driver’s License or ID
4. Military Discharge Papers (DD214) if you have ever served active duty in the Armed Services
5. Be physically able to perform the essential duties of the shipbuilding discipline requested or assigned
6. Be able to obtain the proper security clearance and be a United States person
1. Go to hii.com/careers
2. Navigate to the search bar, type Apprentice, select Ingalls Shipbuilding Division and search jobs
4. Click on the job vacancy to complete the application process
All applicants will be screened by the Ingalls Shipbuilding Employment Office for security and employability. Employment will contact applicants if they are denied employment. Online applications are then sent to the Ingalls Apprentice School Admissions Office for further screening and educational verification. If an applicant meets the requirements, they are then called for an intake interview, where original documents must be submitted. Applicants must submit an online application.
1. Be at least 18 years of age
2. Submit High School Transcript or GED Transcript with test scores
3. State issued Driver’s License or ID
4. Military Discharge Papers (DD214) if you have ever served active duty in the Armed Services
5. Be physically able to perform the essential duties of the shipbuilding discipline requested or assigned
6. Be able to obtain the proper security clearance and be a United States person
1. Go to hii.com/careers
2. Navigate to the search bar, type Apprentice, select Ingalls Shipbuilding Division and search jobs
4. Click on the job vacancy to complete the application process
All applicants will be screened by the Ingalls Shipbuilding Employment Office for security and employability. Employment will contact applicants if they are denied employment. Online applications are then sent to the Ingalls Apprentice School Admissions Office for further screening and educational verification. If an applicant meets the requirements, they are then called for an intake interview, where original documents must be submitted. Applicants must submit an online application.
1. Be at least 18 years of age
2. Submit High School Transcript or GED Transcript with test scores
3. State issued Driver’s License or ID
4. Military Discharge Papers (DD214) if you have ever served active duty in the Armed Services
5. Be physically able to perform the essential duties of the shipbuilding discipline requested or assigned
6. Be able to obtain the proper security clearance and be a United States person
1. Go to hii.com/careers
2. Navigate to the search bar, type Apprentice, select Ingalls Shipbuilding Division and search jobs
4. Click on the job vacancy to complete the application process
All applicants will be screened by the Ingalls Shipbuilding Employment Office for security and employability. Employment will contact applicants if they are denied employment. Online applications are then sent to the Ingalls Apprentice School Admissions Office for further screening and educational verification. If an applicant meets the requirements, they are then called for an intake interview, where original documents must be submitted. Applicants must submit an online application.
Mississippi Gulf Coast Community College, in partnership with Ingalls Apprentice School, works to meet the training needs of apprentices as outlined by the Bureau of Apprenticeship Training of the U.S. Department of Labor. A person who has completed an approved apprenticeship program may receive credit towards the Associate of Applied Science in Maritime Technology. Other requirements for the AASOE degree are outlined under “Graduation information” on the MGCCC website.
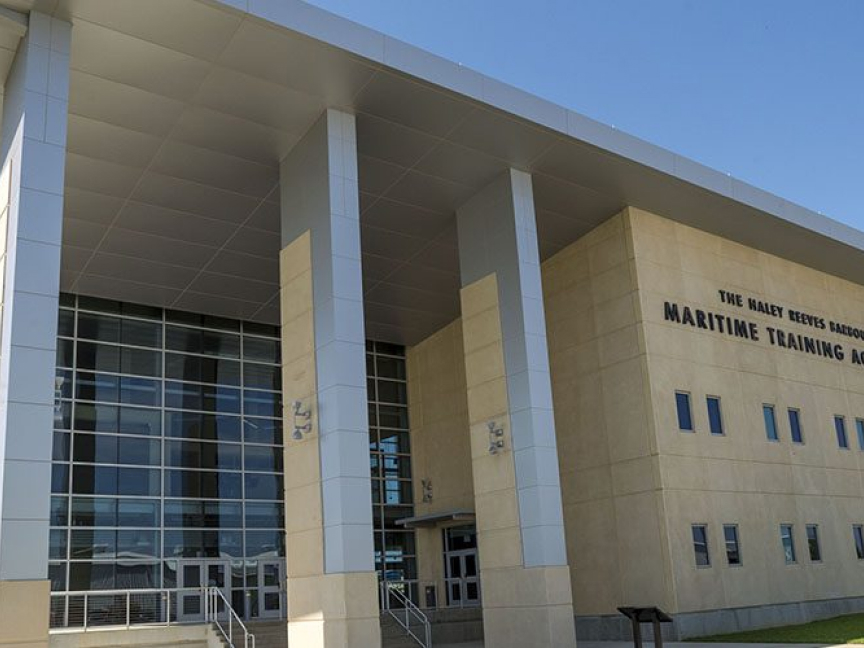





The Ingalls Apprentice School is conveniently housed in the Haley Reeves Barbour Maritime Training Academy on Jerry St. Pe’ Highway off of Highway 90 in Pascagoula, Mississippi. The Training Academy is located across from Ingalls Shipbuilding’s Human Resources building. Named for Haley Reeves Barbour, Mississippi’s 62nd Governor, the newly opened Maritime Training Academy serves as the training epicenter for Ingalls’ Apprentice School. The 70,000 square-foot facility features 24 classrooms, three computer labs, a library, 26 offices/conference rooms and several state-of-the-art craft labs for students to practice the various shipyard trades. Download a map of the Apprentice School
here.
Contact Information:
Sherri Kovar (228) 935-0917
Shelley McElroy (228) 935-7330
LaKres Conner (228) 935-5898

Apprenticeship Programs, Director

Apprentice Class of 1998 – Manager of Workforce Training and Current Electrical Training Manager

Apprentice Class of 2011 – Lead Electrical Instructor

Apprentice Class of 1988 – Pipe and Machinery Training Manager

Apprentice Class of 2001 – Shipfitting, Welding, Sheetmetal, Joiner, Insulation, Carpentry, Paint and Rigging Training Manager

Apprenticeship Administration

Apprenticeship Administration

Apprenticeship Administration







































Thank you.
Your submission was successful.